Discover the most interesting 12+ types of listening with examples in this blog and learn more about listening that will help you gain more understanding of listening concepts.
Listening is a fundamental skill that transcends mere hearing; it involves active engagement and understanding. It is a dynamic process, and people employ various types of listening in their daily interactions to cater to different situations and objectives.
In this blog, we’ll explore the 12+ types of listening with examples; we delve into each style that illustrates their practical applications. Let’s dive into:
What Is Listening?
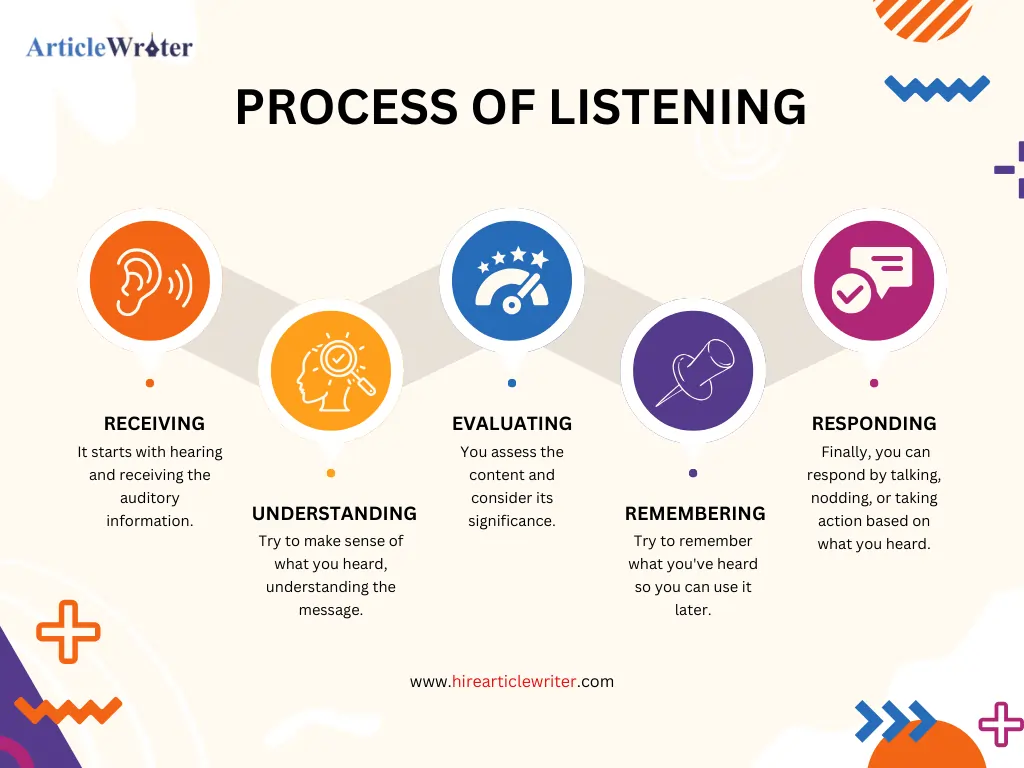
Listening is actively receiving, interpreting, and understanding auditory information, generally conveyed through spoken words, sounds, or other forms of communication. It is a fundamental component of effective communication, allowing individuals to engage with and understand the messages, ideas, emotions, and intentions expressed by others. Effective listening entails hearing the words spoken and processing and making sense of the information, including nuances like tone, inflection, and nonverbal cues, to deepen understanding and facilitate meaningful interactions.
Also Read: 13+ Most Innovative Teaching Strategies In Mathematics
Now, let’s learn about the process of listening.
Process Of Listening
List of 12 Types of Listening with Examples
In the above, we have explained the meaning of listening. Now, we’ll explore 15 distinct types of listening with examples.
1. Active Listening
Active listening involves giving your full attention to the speaker, demonstrating interest, and providing feedback to ensure you understand their message accurately.
Example: In a therapy session, a psychologist actively listens to a client’s feelings and experiences, offering verbal cues like, “I see what you mean,” to show engagement.
2. Empathetic Listening
Empathetic listening is about understanding and sharing the feelings and emotions of the speaker, fostering empathy and emotional support.
Example: When a close friend recounts a personal loss, empathetic listening involves saying, “I can’t imagine how difficult this must be for you,” to show compassion and understanding.
3. Selective Listening
Selective listening involves focusing on specific details or keywords while ignoring other information, a helpful approach for sifting essential information from distractions.
Example: During a business presentation, a listener practices selective listening by concentrating on key figures and data points relevant to their project.
4. Judgmental Listening
Judgmental listening entails forming quick judgments or opinions about the speaker’s message, which can create communication barriers.
Example: During a political debate, a viewer practicing judgmental listening might immediately dismiss one candidate’s arguments based on their preconceived notions.
5. Interruptive Listening
Interruptive listening involves frequently interrupting the speaker, which can be perceived as disrespectful and disruptive.
Example: In a classroom, a student interruptively listens to the teacher, constantly asking questions without letting the teacher complete explanations.
6. Reflective Listening
Reflective listening involves paraphrasing or summarizing the speaker’s words to confirm understanding and clarify shared information.
Example: In a counseling session, the therapist might say, “So, if I understand correctly, you’re saying that you feel overwhelmed due to work-related stress.”
7. Problem-Solving Listening
Problem-solving listening offers practical solutions or advice when someone presents their problems.
Example: A coworker discusses work-related challenges, and a colleague practicing problem-solving listening provides suggestions like, “Have you considered trying this approach to resolve the problem?”
8. Sympathetic Listening
Sympathetic listening provides emotional support and comfort to the speaker without necessarily offering solutions. It acknowledges their feelings and emotions.
Example: A friend shares their struggles, and sympathetic listening involves saying, “I’m here for you, and I can see how much this is hurting you.”
9. Nonverbal Listening
Nonverbal listening focuses on interpreting the speaker’s body language, facial expressions, and gestures to understand unspoken cues and emotions.
Example: During a job interview, an employer practices nonverbal listening by observing candidates’ posture and facial expressions to assess their confidence and enthusiasm.
10. Critical Listening
Critical listening involves evaluating the speaker’s message, and looking for logical inconsistencies, biases, or hidden agendas, typically in decision-making or analytical contexts.
Example: In a scientific conference, critical listening involves questioning the methodology and sources used in a research presentation to ensure credibility.
11. Appreciative Listening
Appreciative listening is about enjoying and savoring shared content, such as music, stories, or entertainment.
Example: Attending a live music concert, the audience practices appreciative listening by relishing the melodies, rhythms, and lyrics of the performance.
12. Informative Listening
Informative listening seeks to acquire specific information or knowledge from the speaker, often used in educational or research contexts.
Example: Students in a lecture practice informative listening to gather information for an upcoming exam, focusing on key concepts and facts.
13. Persuasive Listening
Persuasive listening involves critically evaluating a speaker’s argument with the intent to understand, evaluate, and potentially be swayed by their viewpoint.
Example: During a political debate, an audience member uses persuasive listening to assess each candidate’s arguments before deciding whom to support.
14. Therapeutic Listening
Therapeutic listening is a form of active listening used in medicinal or counseling settings to help clients explore their thoughts, emotions, and concerns.
Example: A patient in a therapy session discusses their anxiety, and the therapist employs therapeutic listening techniques to guide the conversation and provide support.
15. Public Listening
Public listening focuses on understanding and interpreting the opinions, needs, and feedback of a larger audience, such as customers or constituents.
Example: A company monitors social media channels to engage in public listening, and analyzing customer comments and feedback to improve products and services.
These 15 types of listening with examples show the diverse ways in which listening can be employed to foster effective communication and better understand the perspectives and needs of others. Tailoring your listening style to the specific context and goals of the interaction can lead to more productive and meaningful communication.
Also Read: 51+ Best ICT Micro Project Topics: A Complete Checklist
Now, let’s learn about the impact of better listening.
The Impact of Better Listening
The impact of better listening in both personal and professional contexts cannot be overstated. Strong listening skills can lead to numerous positive outcomes and significantly enhance various aspects of your life. Here are some key ways in which better listening can make a difference:
Improved Relationships
Active and empathetic listening fosters deeper connections. When people feel heard and understood, trust and rapport are established, strengthening relationships in personal and professional spheres.
Conflict Resolution
Good listeners who can empathize with different viewpoints, making it easier to resolve conflicts. By understanding the concerns of all parties involved, you can work towards finding mutually beneficial solutions.
Increased Empathy
Listening empathetically allows you to put yourself in someone else’s shoes, enabling you to comprehend their emotions and experiences. This heightened empathy promotes compassion and understanding, leading to more compassionate interactions.
Enhanced Learning
Active listening is crucial for learning and retaining information. Listening attentively allows you to absorb new concepts more effectively, whether in educational settings, professional development seminars, or casual conversations.
Increased Productivity
In professional settings, improved listening skills can boost productivity. Clear instructions and effective communication result in fewer misunderstandings and errors, leading to more efficient workflows.
Building Trust and Credibility
When you listen sincerely, others perceive you as trustworthy and reliable. Trust is the foundation of any healthy relationship, personal or professional. Better listening helps build credibility over time.
Enhanced Communication
Better listening leads to more effective and efficient communication. By giving your full attention to the speaker and actively engaging with them, you are more likely to understand their message accurately. This reduces misunderstandings and promotes clarity in your conversations.
How Can Your Listening Style Impact Your Communication?
Your personal listening style can profoundly impact your communication in various ways. How you listen can influence the quality of your interactions and the level of understanding you achieve. Here’s how your listening style can impact your communication:
1. Engagement and Interest
Active listeners who show genuine interest in what the speaker is saying tend to have more engaging and constructive conversations. They are seen as attentive and interested, encouraging open and meaningful communication.
2. Empathy and Understanding
Empathetic listeners who focus on understanding and sharing the speaker’s emotions build deeper connections. They can offer emotional support and connect more profoundly, fostering empathy in the communication process.
3. Efficiency and Accuracy
Selective listeners may miss critical context or details while effectively filtering essential information. This can lead to misunderstandings and inefficiencies in communication.
4. Openness and Trust
A non-judgmental listening style fosters open and honest dialogue. Listeners who avoid forming quick judgments are likelier to create a safe and trusting environment for effective communication.
5. Clarity and Confirmation
Reflective listeners clarify information by paraphrasing or summarizing the speaker’s words, ensuring mutual understanding. This style minimizes the risk of miscommunication.
6. Personal Development
Recognizing your preferred listening style allows you to work on areas where you need improvement. Developing a more diverse listening skill set can enhance your overall communication abilities.
7. Critical Thinking
Critical listeners are valuable in evaluating the logic and validity of arguments and information. This style is particularly useful in problem-solving discussions, debates, or decision-making processes.
5 Ways To Improve Your Listening
Improving your listening skills is a valuable endeavor to enhance your communication and relationships. Here are five ways to improve your listening.
1. Practice Active Listening
Active listening is a key element of effective listening. It involves giving your full attention to the speaker, asking questions for clarification, and providing feedback to show that you are engaged in the conversation. To practice active listening:
- Maintain eye contact with the speaker.
- Use verbal and nonverbal cues such as nodding and affirmative sounds (e.g., “I see,” “I understand”) to show your engagement.
- Avoid interrupting or formulating your response while the speaker is talking.
2. Minimize Distractions
Distractions can hinder your ability to listen attentively. To minimize distractions:
- Choose a quiet and comfortable environment for the conversation.
- Turn off or silence electronic devices to avoid interruptions.
- Focus on the speaker and the conveyed message, disregarding other thoughts or tasks.
3. Develop Empathetic Listening
Empathetic listening involves understanding and sharing the feelings and emotions of the speaker. To become a more empathetic listener:
- Practice putting yourself in the speaker’s shoes and trying to understand their perspective.
- Use empathetic statements to express your understanding and support, such as, “I can imagine how that must have felt.”
Also Read: 25+ Creative Atom Project Ideas For Students In 2024
4. Avoid Premature Judgment
Judgmental listening can hinder effective communication. To avoid forming quick judgments while listening:
- Suspend your judgments until you have heard the speaker’s complete message.
- Be open to diverse perspectives and consider the context and background of the speaker’s viewpoint.
5. Reflective Listening
Reflective listening involves paraphrasing or summarizing the speaker’s words to confirm your understanding. To practice reflective listening:
- Periodically repeat what you’ve heard in your own words to the speaker.
- Ask the speaker for clarification if you are unsure about any part of their message.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the types of listening with examples underscore the rich tapestry of ways in which individuals engage in the act of listening. These various listening styles, from active and empathetic to reflective and critical listening, serve as tools for enhancing communication, fostering understanding, and building meaningful connections. The examples provided illustrate how these listening styles can be applied in different contexts: strengthening personal relationships, resolving conflicts, learning, making informed decisions, or engaging in productive discussions.
Recognizing and understanding the various listening styles empowers individuals to adapt their methods to meet better the needs of specific situations and the people they are communicating with. With these listening skills and choosing the appropriate style for each method, individuals can become more effective and understanding communicators, leading to more balanced relationships and better outcomes in both personal and professional life.
Thank you for reading our article about types of listening with examples.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Why is listening important for effective communication?
Listening is essential for effective communication because it is a two-way exchange of information. It shows respect for the speaker, fosters understanding, and helps avoid misunderstandings. Good listening promotes empathy, strengthens relationships, and leads to more productive and meaningful interactions.
Q2. What are the 3 A’s of active listening?
Listening is not the same as hearing. Listening is a conscious activity based on three basic skills: attitude, attention, and adjustment. These skills are known collectively as triple-A listening. A positive attitude paves the way for open-mindedness.
Q3. What is a responsive listener?
Responsive listeners demonstrate to the speaker that they are listening and understanding what is being said, encouraging the speaker to continue. Encouraging responses may include both nonverbal and verbal cues: Nonverbal Responses.